Click to Enlarge Image
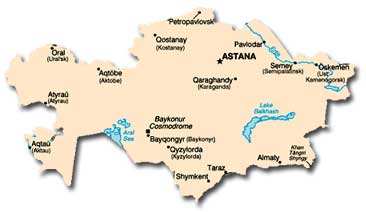
Location: Kazakhstan is located in the center of the continent of
Asia, with a coastline only on the landlocked Caspian Sea. Russia
forms its entire northern border.

Click to Enlarge Image
Size: At 2,717,000 square kilometers, Kazakhstan’s area is about four times that of Texas, making Kazakhstan the ninth largest nation in the world. Some 47,500 kilometers of the total area is occupied by bodies of water.
Land Boundaries: Kazakhstan has common borders with the following countries: China (1,533 kilometers), Kyrgyzstan (1,051 kilometers), Russia (6,846 kilometers), Turkmenistan (379 kilometers), and Uzbekistan (2,203 kilometers).
Length of Coastline: Kazakhstan’s only coastline runs 1,894 kilometers along the landlocked Caspian Sea.
Maritime Claims: Jurisdiction over oil, natural gas, and other resources in the Caspian Sea is in dispute with other littoral states.
Topography: Kazakhstan’s topography varies considerably by region. In the east and northeast, about 12 percent of its territory is occupied by parts of the Altay and Tian Shan mountain ranges with elevations of up to 6,995 meters. More than three-quarters of the country is desert or semi-desert, with elevations less than 500 meters. Along the Caspian Sea, elevations are below sea level.
Principal Rivers: Seven of Kazakhstan’s rivers are 1,000 kilometers or more in length: the Chu, Emba, Ili, Irtysh, Ishim, Syr-Darya, and Ural. The Irtysh and Ural rivers flow partly through Kazakhstan and partly through Russia. The Ili River flows from China into Lake Balkhash in eastern Kazakhstan. The Syr-Darya flows from eastern Uzbekistan across Kazakhstan into the Aral Sea.
Climate: Because Kazakhstan has no exposure to maritime weather patterns, the entire country has a continental climate featuring cold winters and hot summers. Rainfall, which varies from 100 to 200 millimeters per year, generally is heavier in the south and in the eastern mountains.
Natural Resources: Although estimates of Kazakhstan’s hydrocarbon resources were reduced in 2004, the country is believed to possess about 1 percent of the world’s total reserves of natural gas and petroleum. Also present are significant reserves of chromium, coal, copper, gold, lead, tungsten, and zinc. Substantial amounts of good agricultural land are present, although Soviet and post-Soviet agricultural practices have substantially reduced the extent of that land.
Land Use: In 2001 some 8 percent of land was rated as arable, a reduction from the 1998 estimate of 11.2 percent. Less than 0.1 percent of that land was under permanent crops. About 4.8 percent is forest and woodland. The remainder is pastureland, meadows, desert, and mountains. In 2001 irrigated land totaled an estimated 24,000 square kilometers.
Environmental Factors: Most of Kazakhstan’s water supply has been polluted by industrial and agricultural runoff and, in some places, radioactivity. The Aral Sea, which is shared with Uzbekistan, has shrunk to three separate bodies of water because of water drawdowns in its tributary rivers. A Soviet-era biological weapons site is a threat because it is located on a former island in the Aral Sea that is now connected with the mainland. The reduction in the Aral Sea’s water surface has exacerbated regional climatic extremes, and agricultural soil has been damaged by salt deposits and eroded by wind. Desertification has eliminated substantial tracts of agricultural land. Plants in industrial centers lack controls on effluents into the air and water. The Semey region in the northeast has long-term radiation contamination from Soviet-era weapons testing. The Ministry of Environmental Protection is underfunded and given low priority. Some new environmental regulation of the oil industry began in 2003, but new oil operations on Kazakhstan’s Caspian coast add to that sea’s already grave pollution. International programs to save the Aral and Caspian seas have not received meaningful cooperation from Kazakhstan or other member nations.
Time Zones: Kazakhstan has three time zones, which are, respectively, five, six, and seven hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time.